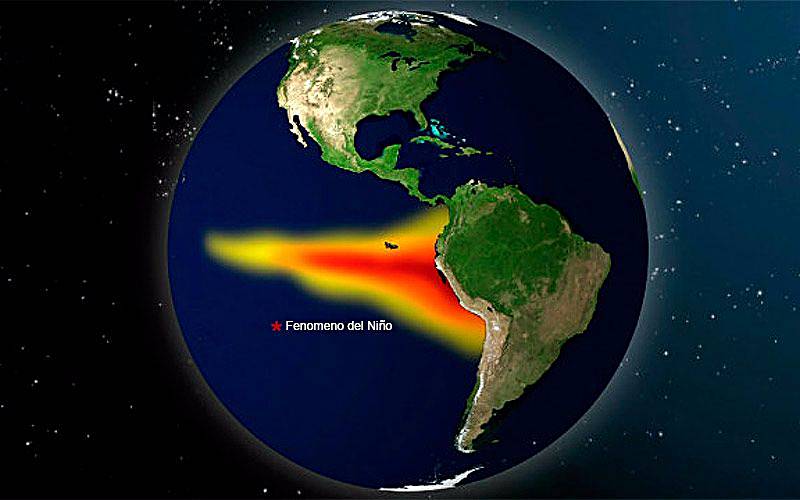
El Niño is a climate pattern that occurs irregularly, but on average every 2 to 7 years, in which the Pacific Ocean’s surface temperatures become warmer than normal. This warming can affect weather patterns and ocean currents around the world. In Ecuador, El Niño can have a significant impact on weather patterns and ecosystems.
One of the most noticeable effects of El Niño in Ecuador is increased rainfall. During El Niño years, the country can experience heavy rains and flooding, particularly in coastal regions. This can cause damage to infrastructure and crops, as well as lead to displacement of communities.

El Niño’s Impact on Ecuador
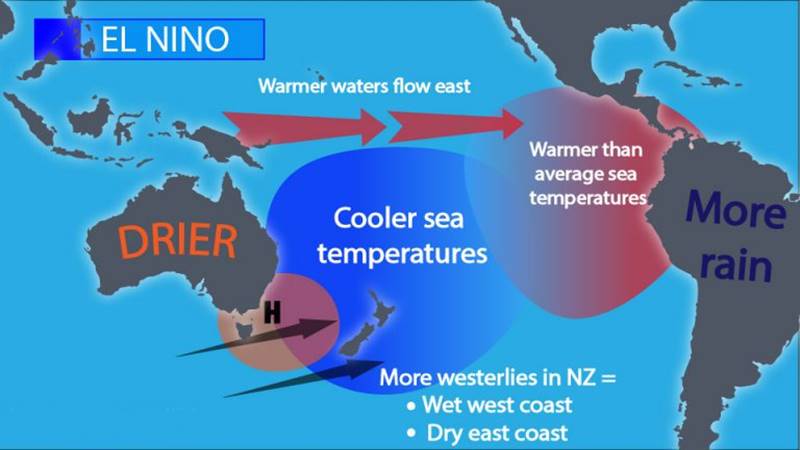
In addition to heavy rainfall, El Niño can also lead to warmer temperatures in coastal regions of Ecuador. This can have implications for both ecosystems and tourism. Warmer waters can disrupt the marine food chain and lead to reduced fish populations, which can impact fishing industries. On the other hand, warmer temperatures can make beach destinations more appealing to tourists.
Another potential impact of El Niño in Ecuador is increased risk of landslides and erosion. Heavy rainfall can destabilize soils and lead to dangerous landslides in mountainous areas. This can cause significant damage to homes and infrastructure, as well as pose a threat to human safety.

Despite the potential negative effects of El Niño, there are also some benefits. Increased rainfall can lead to improved soil moisture and crop yields, which can be beneficial for agriculture. Additionally, warmer waters can attract certain fish species that are more desirable for fishing.
Overall, the impact of El Niño on Ecuador can be significant, both in terms of negative and positive effects. The government and communities take measures to prepare for and respond to the impact of El Niño, including early warning systems, infrastructure improvements, and emergency response plans.
Looking to expand your knowledge about Ecuador? Check out our Everything Ecuador Page!